เขียนโปรแกรมภาษา Python ด้วย Google Colab ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม
เรียน Python ด้วย Google Colab ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม
เขียนโปรแกรมภาษา Python ปูพื้นฐานเข้มข้น
เอกสารประกอบการเรียน https://www.glurgeek.com/education/pythoncolab/
เข้าเรียน Python Programming with Google Colab ปูพื้นฐานเข้มข้น ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม EP.1 – EP.14
➡️ https://bit.ly/pythoncolab2022
💗 สิทธิพิเศษสำหรับสมาชิก Membership 💗
🟡 Gold Supporter 🟢 Premium Supporter
สามารถเข้ารับชมคลิปได้แบบไม่จำกัด
วิธีการเข้าบทเรียนไปที่ https://www.youtube.com/ajnesttheseries
กดที่ JOIN/สมัคร ➡️ Gold Supporter หรือ Premium Supporter ➡️ ทำการสมัครเข้าเรียน
🔔 สามารถเรียนได้ทุกคน ไม่จำเป็นต้องมีความรู้ด้านการเขียนโปรแกรมมาก่อน
เนื้อหาการเรียน Python Programming with Google Colab การเขียนโปรแกรมภาษาไพธอน 2022
EP.1 เริ่มต้นใช้งาน Google Colab เขียนโปรแกรมภาษา Python ปูพื้นฐานเข้มข้น
EP.2 Python Syntax เรียนรู้โครงสร้างการเขียนโปรแกรมภาษาไพธอน
EP.3 Python Variables เขียนโปแกรมสร้างตัวแปรภาษาไพธอน
EP.4 Python Operations เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างตัวดำเนินการภาษาไพธอน
EP.5 Python Conditional Control Statements เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างคำสั่งเงื่อนไขภาษาไพธอน
EP.6 Python Conditional and Loop Statements เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างคำสั่งเงื่อนไขและลูปภาษาไพธอน
EP.7 Python Loop Statements เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างคำสั่งลูปภาษาไพธอน
EP.8 Python String เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างข้อความภาษาไพธอน
EP.9 Python String Formatting เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างรูปแบบของข้อความภาษาไพธอน
EP.10 Python Lists เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลแบบลิสต์ภาษาไพธอน
EP.11 Python Dictionary เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลแบบดิกชันนารีภาษาไพธอน
EP.12 Python Tuple เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลแบบทูเพิลภาษาไพธอน
EP.13 Python Set เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลแบบเซ็ตภาษาไพธอน
EP.14 Python Functions เขียนโปรแกรมสร้างฟังก์ชันใช้เอง
เข้าเรียน Python Data Wrangling with Pandas Workshops ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม Workshop 1 – Workshop 14
➡️ https://bit.ly/pythonwrang2022
เข้าเรียนการเขียนโปรแกรมด้วย Flowgorithm ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม EP.1 – EP.8
➡️ https://bit.ly/flowpro2022
เข้าเรียน C Programming ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม EP.1 – EP.40
➡️ https://bit.ly/cpro2022
เข้าเรียน JavaScript Programming ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม Ex1 – Ex14
➡️ https://bit.ly/jspro2022
เข้าเรียน SQL Database Programming ฉบับคนไม่เคยเขียนโปรแกรม EP.1 – EP.13
➡️ https://bit.ly/sqlpro2022
เข้าเรียน RapidMiner Studio for Data Science ฉบับปูพื้นฐานเข้มข้น EP.1 – EP.10
➡️ https://bit.ly/rapid2022
เข้าเรียน Tableau for Beginners ฉบับปูพื้นฐานเข้มข้น EP.1 – EP.15
➡️ https://bit.ly/tableau2022
เข้าเรียน Tableau for Intermediate ฉบับเทคนิคเข้มข้น EP.1 – EP.26
➡️ https://bit.ly/tableauinter2022
😀 หากคลิปนี้เป็นประโยชน์กับท่านช่วยกด Subscribe เพื่อติดตามและเป็นกำลังใจในการทำคลิปต่อไปด้วยนะครับ ❤️
🎥📍 http://bit.ly/ajnesttheseriesSubscribe
Aj. NesT the Series Channel คือ ช่อง YouTube ที่เน้นสาระการเรียนรู้เพื่อฝึกให้ผู้เรียนพัฒนาตนเองทางด้านการศึกษาเทคโนโลยีคอมพิวเตอร์ การพัฒนาการเขียนโปรแกรมทั้งระดับฮาร์ดแวร์และซอฟต์แวร์ การพัฒนางานทางด้านวิศวกรรมและวิทยาศาสตร์ วิทยาการข้อมูล และสร้างสิ่งประดิษฐ์นวัตกรรมต่าง ๆ ที่มีประโยชน์ได้ด้วยตนเองไปพร้อมกับความสนุกสนานและความเข้าใจที่มุ่งหวังให้ผู้เรียนได้นำความรู้เหล่านี้ไปต่อยอดและประยุกต์ใช้เพื่อเพิ่มความสามารถของตนเองในการประกอบอาชีพได้
▲ ติดตามช่องของเราได้ที่: http://bit.ly/ajnesttheseriesSubscribe
▲ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ajnesttheseries
▲ Website: https://www.glurgeek.com
▲ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/ajnesttheseries
▲ Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/ajnesttheseries
#ajnesttheseries #ajnestสอนpython #pythongooglecolab #pythonprogramming
Python Programming
● Python is an open-source, object-oriented, high-level powerful programming language.
● Developed by Guido van Rossum in the early 1990s. Named after Monty Python
● Python source code is also available under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
● Available for download from http://www.python.org.
ทำไมต้อง Pyhton?
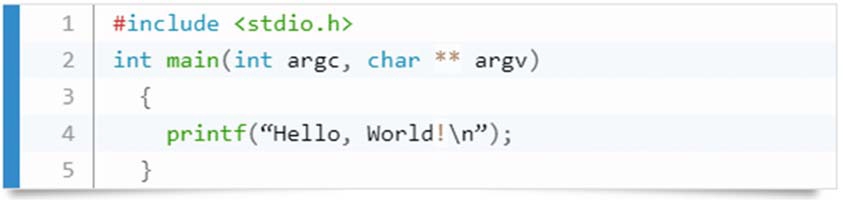
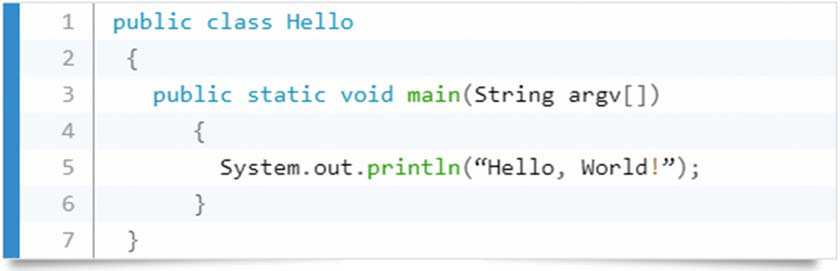
Python Is Easy to Use
C Program
C++ Program

Java Program
Python Program

ใครใช้ Python บ้าง?
Organizations Using Python
Web Development: Yahoo Maps, Yahoo Groups, Google, Zope Corporation, Ultraseek, Linux Weekly News, ElasticHosts Cloud Servers, Mojam.com, hunch, Shopzilla, Movieplayer.it, Multiplayer.it.
Games: Battlefield 2, Crystal Space, Star Trek Bridge Commander, The Temple of Elemental Evil, Vampire: The Masquerade: Bloodlines, Civilization 4, QuArK (Quake Army Knife)
Graphics: Industrial Light & Magic, Walt Disney Feature Animation, HKS, Inc. (ABAQUS/CAE), RoboFog, Caligari Corporation, Blender 3D, Jasc Software, Paint Shop Pro.
Financial: Altis Investment Management, ABN AMRO Bank, Treasury Systems, Bellco Credit Union, Journyx Timesheet, and Resource Management Software.
Science: National Weather Service, Radar Remote Sensing Group, Applied Maths, Biosoft, The National Research Council of Canada, Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) Theoretical Physics Division, AlphaGene, Inc., LLNL, NASA, Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute (SMHI), Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI), Objexx.
Engineering, Nmag Computational Micromagnetics Electronic Design Automation : Ciranova, Productivity Design Tools, Object Domain, Pardus, Red Hat, SGI, Inc., MCI Worldcom, Nokia.
Education: University of California, Irvine, Smeal College of Business, The Pennsylvania State University, New Zealand Digital Library, IT Certification Exam preparation, SchoolTool.
Business Software: Raven Bear Systems Corporation, Thawte Consulting, Advanced Management Solutions Inc., IBM, Arakn, RealNetworks, dSPACE, Escom, The Tiny Company, Nexedi, Piensa Technologies – Bufete Consultor de Mexico, Nektra, WuBook.
To see the details of the above organizations
https://wiki.python.org/
Google Colab
Google has done the coolest thing ever by providing a free cloud service based on Jupyter Notebooks that supports free GPU. Not only is this a great tool for improving your coding skills, but it also allows absolutely anyone to develop deep learning applications using popular libraries such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, Keras, and OpenCV.
https://colab.research.google.com/
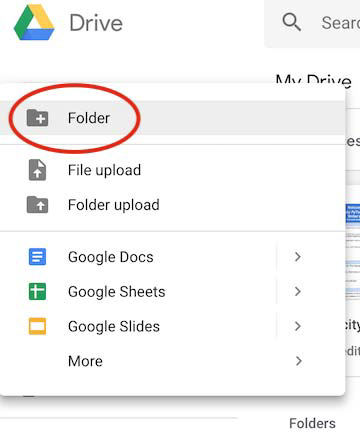
How to use – setting up your drive for using Google Colab.
Google Drive –> More –> Colaboratory
Otherwise, you can always go directly to Google Colab.
Python Programming with Colaboratory
1. Python Syntax
Ex1 Python Line Structure
x = -2
if x>0:
print("I love Python Programming")
else:
print("I love Java Programming")
Ex2 Comments in Python
x = 6
if x>0:
#print("I love Python Programming")
print("ฉันรักภาษาไพธอน")
else:
"""print("I love Java Programming")
print("I love C Programming")"""
print("I love C#.NET Programming")
Ex3 Joining Two Lines
a = 0
b = 1
c = 2
d = 3
e = 4
f = 5
if a==0 and b>0 \
and c>1 and d>2 \
and e>3 and f>4:
print("Joining Two Lines --> I love Python Programming")
Ex4 Indentation
x=2
if x>0:
print("Space bar in Python")
else:
print("Smile :D")
print("A single space indentation")
2. Python Variable
Ex5 Python Assignment Statements
Name = "Python Programming" #String Qty = 9 #Integer Value = 9000.89 #Floating Point print(Name) print(Qty) print(Value)
Ex6 Multiple Assignment
x = y = z =9 a = 6 b = 3 c = 99 '''print(x) print(y) print(z)''' print(x,y,z) print(a) print(b,c)
Ex7 Multiple Assignment 2
x = y = z =9 a, b, c = 6, 3, "I love Python Programming" '''print(x) print(y) print(z)''' print(x,y,z) print(a, b) print(c)
Ex8 Swap Variables
x = 80 y = 90 print(x) print(y) x, y = y, x print(x) print(y)
Ex9 Local and Global Variables in Python (1)
var1 = "Python"
def func1():
var1 = "Java"
print("In side func1() var1 = ", var1)
def func2():
print("In side func2() var1 = ", var1)
func1()
func2()
Ex10 Local and Global Variables in Python (2)
def func1():
global var1
var1 = "Java"
print("In side func1() var1 = ", var1)
def func2():
print("In side func2() var1 = ", var1)
func1()
func2()
3. Operators and Operands
Ex26 Python Arithmetic Operators
x = 16
y = 9
z_add = x+y
print("x+y = ", z_add)
z_sub = x-y
print("x-y = ", z_sub)
z_mul = x*y
print("x*y = ", z_mul)
z_div = x/y
print("x/y = ", z_div)
z_mod = x%y
print("x%y = ", z_mod)
z_power = x**y
print("x**y = ", z_power)
z_floor = x//y
print("x//y = ", z_floor)
Ex27 Python Comparison Operators
x = 13 y = 16 z_equal = x==y print(z_equal) z_notequal = x!=y print(z_notequal) z_greater = x>y print(z_greater) z_less = x<y print(z_less) z_greatereq = x>=y print(z_greatereq) z_lesseq = x<=y print(z_lesseq)
Ex28 Python Logical Operators
x = 9 y = 15 z_and = (x>10 and y>10) print(z_and) z_or = (x>10 or y>15) print(z_or) z_not = not(x>10 and y>10) print(z_not)
Ex29 Python Assignment Operators
x = 16 y = 9 x+=y #x = x + y print(x) x-=y #x = x - y print(x) x*=y #x = x * y print(x) x/=y #x = x / y print(x) x%=y #x = x % y print(x) x**=y #x = x^y print(x) x//=y #x = x//y print(x)
4. Python if elif else
Ex30 if…else Statement
a = 30
if(a>20):
print("Value of a is greater than 20")
else:
print("Value = 20 หรือ Value < 20")
Ex31 if .. elif .. else Statement
var1 = {"Class":"Python", "Section":'A', "Roll_No":16}
if(type(var1) == int):
print("Integer")
elif(type(var1) == float):
print("Float")
elif(type(var1) == complex):
print("Complex")
elif(type(var1) == bool):
print("Boolean")
elif(type(var1) == str):
print("String")
elif(type(var1) == tuple):
print("Tuple")
elif(type(var1) == dict):
print("Dictionaries")
elif(type(var1) == list):
print("List")
else:
print("Unknown")
Ex32 Nested if .. else Statement
age = 18
if(age >= 11):
print("You are eligible to see the Football match.")
if(age <= 20 or age >= 60):
print("Ticket price is 1,200 Baht")
else:
print("Ticket price is 2,000 Baht")
else:
print("You're not eligible to buy a ticket.")
Ex33 Use the and operator in an if Statement
x = True
y = True
if x and y:
print('Both x and y are True')
else:
print('x is False or y is False or Both x and y are False')
Ex34 Use the in operator in an if Statement
s = 'Ruby' l = ['Java', 'Python', 'C#', 'C++', 'PHP', 'HTML5', 'Ruby'] if s in l: print(s + ' Tutorial') if s == 'Java' or s == 'Python' or s == 'C#' or s == 'Ruby': print(s + ' Tutorial')
Ex35 Write an if-else in a single line of code
x = 160 print(x) result = x*9 if x > 600 else x / 9 print(result)
Ex36 Define a negative if
x = 70
print(x)
if not x == 70:
print('The Value of x different from 70')
else:
print('The Value of x is equal to 70')
5. Python for loop
Ex37 for loop
color_list = ["Yellow", "Blue", "Green", "Black"] for color in color_list: print(color)
Ex38 Python for loop and range() function
for a in range(4):
print(a)
print("\n")
for a in range(2,7): #[2,7)
print(a)
print("\n")
for a in range(2,23,5):
print(a)
6. Python while loop
Ex40 while loop
x = 0 while(x<=9): print(x) x += 1 #x = x + 1
Ex41 Python: while and else Statement
x = 0
result = 0
while(x<10):
result = result + x
x = x + 1
else:
print('The sum first 9 integers: ', result)
print(0+1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9)
Ex42 while loop with if-else and break Statement
x = 1
result = 0
while(x<10):
result = result + x
x = x + 1
if(x==5):
break
else:
print('The sum of first 9 integers: ', result)
print('The sum of ',x,' numbers is :', result)
7. Python String
Ex46 Initialize string literals in Python
s = "I'm a Programmer"
print(s)
s1 = "'I love Python Programming'"
print(s1)
s2 = "I'm a Programmer, 'I love Python Programming'"
print(s2)
s3 = 'dir "c:\&temp\*.sas" /o:n /b > "c:\&temp\python.txt"'
print(s3)
s4 = """ Python Exercises
C Tutorial
Java Tutorial and Exercises ..."""
print(s4)
s5 = '\n\t Python Exercises\n \t C Tutorial\n \t Java Tutorial and Exercises ...'
print(s5)
Ex47 Access character(s) from a String
a = "I'm a Programmer" print(a) b = a[2] print(b) c = a[6] print(c) d = a[4+3] print(d) a0 = a[0] print(a0) a1 = a[-1] print(a1) a2 = a[-2] print(a2) a3 = a[15] print(a3) print(a[0:6]) #[0:6) or [0:5] print(a[3:9]) print(a[:8]) print(a[3:])
Ex48 Python String concatenation and Using ‘*’ operator
a = "Python" + "Programming" print(a) b = "<" + a*6 + ">" print(b) c = "Python" d = "Programming" c+=d #c = c + d print(c)
Ex49 Python strings as immutable
a = "PYTHON" b = "x" + a[0:] print(b)
Ex50 String Length
a = "Python Programming" len(a) print(a[17]) print(a[0]) print(a[11])
Ex51 Traverse string with a while loop
a = "PROGRAMMING"
i = 0
while i < len(a):
b = a[i]
print(b)
i = i + 1
Ex52 Traverse string with a for loop
a = "PROGRAMMING"
i = 0
new = " "
for i in range (0, len(a)):
b = a[i]
new = new + b
i = i + 1
print(b)
print(new)
Ex53 Search a character in a string
def search(char,str):
L = len(str)
print(L)
i = 0
while i < L:
if str[i] == char:
return 1
i = i + 1
return -1
print(search("P", "PYTHON"))
Ex54 String Formatting 1
#Syntax: str.format(*args, **kwargs)
#Basic Formatting
a = '{}{}'.format('Python', 'Programming')
print(a)
b = '{} {}'.format('Python', 'Programming')
print(b)
c = '{} {}'.format(20, 80)
print(c)
d = '{1} {0}'.format('Python', 'Programming')
print(d)
#Padding and Aligning Strings
#Aligh Right
e = '{:>15}'.format('Python')
print(e)
f = '{:>20}'.format('Python')
print(f)
#Aligh Left
g = '{:15}'.format('Python')
print(g)
#By Argument
h = '{:<{}s}'.format('Python', 15)
print(h)
i = '{:*<15}'.format('Python')
print(i)
#Align Center
j = '{:^16}'.format('Python')
print(j)
Ex55 String Formatting 2
#Truncating Long String
a = '{:.10}'.format('Python Tutorial')
print(a)
#By Arguemnt
b = '{:.{}}'.format('Python Tutorial', 10)
print(b)
#Combining Trucating and Padding
c = '{:10.10}'.format('Pyhton Tutorial')
print(c)
e = '{:d}'.format(30)
print(e)
f = '{:f}'.format(3.14689323899)
print(f)
#Padding Numbers
g = '{:5d}'.format(39)
print(g)
h = '{:05.2f}'.format(6.12345678123)
print(h)
#Signed Numbers
i = '{:+d}'.format(39)
print(i)
j = '{: d}'.format((-39))
print(j)
k = '{: d}'.format(39)
print(k)
#Named Placeholders
data = {'first': 'Aj.', 'last': 'NesT'}
l = '{first} {last}'.format(**data)
print(l)
m = '{first} {last}'.format(first='Aj.', last='NesT')
print(m)
#Date Time
from datetime import datetime
n = '{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M}'.format(datetime(2020, 8, 26, 10, 38))
print(n)
8. List
Ex56 Create a Python list
List1 = [6, 9, 12, 16] print(List1) List2 = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green', 'White'] print(List2) List3 = ['Green', 12, 116.16] print(List3) List = [] print(List) #Use + Operator and * Operator color_list1 = ["White", "Yellow"] color_list2 = ["Pink", "Blue"] color_list3 = ["Green", "Black"] color_list = color_list1 + color_list2 + color_list3 print(color_list) number = [1, 2, 3] print(number[2]*4) print(number*4)
Ex57 List indices
color_list = ["Red", "Blue", "Green", "Black", "Yellow"]
print(color_list[0])
print(color_list[1])
print(color_list[2])
print(color_list[3])
print(color_list[4])
#Add an item to the end of the list
color_list.append("White")
print(color_list)
#Insert an item at a given position
color_list.insert(2, "Grey")
print(color_list)
#Modify an element by using the index of he element
color_list[2] = "Pink"
print(color_list)
#Remove an items from the list
color_list.remove("Black")
print(color_list)
#Remove all items from the list
color_list.clear()
print(color_list)
Ex58 List Slices 1
color_list = ["Red", "Blue", "Green", "Black"]
print(color_list[0:2]) #[ )
print(color_list[1:2]) #[0, 1, 2, 3, ...]
print(color_list[1:-1]) #[..., -3, -2, -1]
print(color_list[1:-2])
print(color_list[:3])
print(color_list[:])
color_list.pop(2)
print(color_list)
color_list.index("Red")
color_list.index("Black")
color_list = ["Red", "Blue", "Green", "Black"]
print(color_list)
color_list.append("Green")
print(color_list)
color_list.count("Green")
color_list.append("Blue")
print(color_list)
color_list.count("Blue")
color_list.append("Green")
print(color_list)
color_list.count("Green")
Ex59 List Slices 2
#Sort the items of the list in place
color_list = ["Red", "Blue", "Green", "Black"]
print(color_list)
#Sort
color_list.sort(key=None, reverse=False)
print(color_list)
#Reverse
color_list.sort(key=None, reverse=True)
print(color_list)
color_list.reverse()
print(color_list)
#Copy
color_list.copy()
color_list.index("Green")
color_list.index("Blue")
#Lists are Mutable
print(color_list)
print(color_list[0])
color_list[0] = "White"
print(color_list)
print(color_list[0])
Ex60 List Slices 3
#Convert a list to a tuple in Python listx = [1, 2, 3, 4] print(listx) tuplex = tuple(listx) print(tuplex) #How to use the double colon[::] listx = [3, 13, 6, 9, 18, 2, 10, 1, 16, 4] print(listx) sublist = listx[2:8:2] #list[start:stop:step] print(sublist) sublist = listx[6:2:-2] #list[start:stop:step] print(sublist) print(listx) print(max(listx)) print(min(listx))
Ex61 List Slices 4
#Compare two lists in Python listx1, listx2 = [3, 5 ,7, 9], [3, 5, 7, 9] print(listx1) print(listx2) print(listx1 == listx2) listx1, listx2 = [9, 7, 5, 3], [3, 5, 7, 9] #Create two lists equal, but unsorted. print(listx1 == listx2) listx1, listx2 = [2, 3, 5 ,7], [3, 5, 7, 9] #Create two different lists print(listx1 == listx2) print(listx1.sort() == listx2.sort()) #Order and Compare
Ex62 List Slices 5
#Nested lists in Python listx = [["Hello", "Python"], [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]] print(listx) print(listx[0][1]) #The first [] indicates the index of the outer list. print(listx[1][3]) #The second [] indicates the index nested lists. listx.append([True, False]) #Add new items print(listx) listx[1][2] = 4 print(listx)
Ex63 List Slices 6
#How can I get the index of an element contained in the list?
listY = list("HELLO PYTHON")
print(listY)
index = listY.index("L") #get index of the first item whose value is passed as parameter
print(index)
index = listY.index("T", 4) #define the index from which you want to search
print(index)
index = listY.index("O", 3, 5) #define the segment of the list to be searched
print(index)
Ex64 Using Lists as Stacks
color_list = ["Red", "Blue", "Green", "Black"]
print(color_list)
color_list.append("White")
print(color_list)
color_list.append("Yellow")
print(color_list)
color_list.pop()
print(color_list)
color_list.pop()
color_list.pop()
print(color_list)
Ex65 Using Lists as Queues
from collections import deque
color_list = deque(["Red", "Blue", "Green", "Black"])
color_list.append("White")
print(color_list)
color_list.append("Yellow")
print(color_list)
color_list.popleft() #The first to arrive now leaves
print(color_list)
color_list.popleft() #The second to arive now leaves
print(color_list)
9. Python Dictionary
Ex66 Create a dictionary in Python
#Create a new dictoinary in Python
#Empty dictionary
new_dict = {}
print(new_dict)
#Dictionary with key-value
color = {"col1" : "Red", "col2" : "Green", "col3" : "Orange"}
#Get value by key in Python dictionary
#Declaring a dictionary
dict = {1:20.5, 2:3.03, 3:23.22, 4:33.12}
#Access value using key
dict[1]
dict[3]
#Accessing value using get() method
dict.get(1)
dict.get(3)
#Add key/value to a dictionary in Python
#Declaring a dictionary with a single element
dict = {'python1' : 'DICTIONARY'}
print(dict)
dict['python2'] = 'STRING'
print(dict)
#Using update() method to add key-value pairs in to dictionary
d = {0:10, 1:20}
print(d)
d.update({2:30})
print(d)
Ex67 Iterate over Python dictionaries using for loops
#Iterate over Python dictionaries using for loops
d = {'Red': 1, 'Green': 2, 'Blue': 3}
for color_key, value in d.items():
print(color_key, 'corresponds to', d[color_key])
Ex68 Remove a key from a Python dictionary
#Remove a key from a Python dictionary
myDict = {'a':1,'b':2,'c':3,'d':4}
print(myDict)
if 'a' in myDict:
del myDict['a']
print(myDict)
Ex69 Sort a Python dictionary by key
color_dict = {'red':'#FF0000', 'green':'#008000', 'black':'#000000', 'white':'#FFFFFF'}
for key in sorted(color_dict):
print("%s: %s" % (key, color_dict[key]))
Ex70 Find the maximum and minimum value of a Python dictionary
my_dict = {'x':500, 'y':5874, 'z':560}
key_max = max(my_dict.keys(), key=(lambda k: my_dict[k]))
key_min = min(my_dict.keys(), key=(lambda k: my_dict[k]))
print('Maximum Value: ',my_dict[key_max])
print('Minimum Value: ',my_dict[key_min])
Ex71 Concatenate two Python dictionaries into a new one
dic1 = {1:10, 2:20}
dic2 = {3:30, 4:40}
dic3 = {5:50, 6:60}
dic4 = {}
for d in (dic1, dic2, dic3): dic4.update(d)
print(dic4)
Ex72 Test whether a Python dictionary contains a specific key
fruits = {}
fruits["apple"] = 1
fruits["mango"] = 2
fruits["banana"] = 4
#Use in.
if "mango" in fruits:
print("Has mango")
else:
print("No mango")
#Use in on nonexistent key.
if "orange" in fruits:
print("Has orange")
else:
print("No orange")
Ex73 Find the length of a Python dictionary
fruits = {"mango": 2, "orange": 6}
#Use len() function to get the length of the dicationary
print("Length: ", len(fruits))
10. Python Tuples
Ex74 Create a tuple
#Create an Empty Tuple
tuplex = ()
print(tuplex)
#Create a tuple with different data types
tuplex = ('tuple',False,6.3,2)
print(tuplex)
#Create a tuple with numbers, notation without parenthesis
tuplex = 4, 7, 3, 9, 2
print(tuplex)
#Create a tuple of one item, notation without parenthesis
tuplex = 4,
print(tuplex)
#Create an empty tuple with tuple() function buit-in Python
tuplex = tuple()
print(tuplex)
#Create a tuple from a iterable object
tuplex = tuple([True, False])
print(tuplex)
Ex75 How to get an item of the tuple in Python?
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = ("c", "e", 3, 1, 2, "p", "r", "o", "g", "r", "a", "m", "m","i","n", "g")
print(tuplex)
#get item (3th element) of the tuple by index
item = tuplex[2]
print(item)
#get item (3th element from last) by index negative
item1 = tuplex[-3]
print(item1)
Ex76 How to know if an element exists within a tuple in Python? and List to Tuple
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = ("c", "e", 3, 1, 2, "p", "r", "o", "g", "r", "a", "m", "m","i","n", "g")
print(tuplex)
#Use in statment
print("r" in tuplex)
print(6 in tuplex)
#List to Tuple
#Create List
listx = [6, 12, 8, 4, 15, 3]
print(listx)
#Use the tuple(function buit-in Python, passing as parameter the list)
tuplex = tuple(listx)
print(tuplex)
Ex77 Unpack a tuple in several variables
#Unpack a tuple in several variables #Create a tuple tuplex = 4, 8, 3 print(tuplex) n1, n2, n3 = tuplex #unpack a tuple in variables print(n1 + n2 + n3)
Ex78 Add item in Python tuple!
#Create a tuple tuplex = (4, 6, 2, 8, 3, 9) print(tuplex) #Add value tuplex = tuplex + (9,) print(tuplex) #Adding items in a specific index tuplex = tuplex[:5] + (15, 20, 25) + tuplex[:5] print(tuplex) #Converting the tuple to list listx = list(tuplex) print(listx) #Use differnet ways to add items in list listx.append(30) print(listx) tuplex = tuple(listx) print(tuplex)
Ex79 Clone a tuple
from copy import deepcopy
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = ("PYTHON", 6, [], True)
print(tuplex)
#Make a copy of a tuple using deepcopy() function
tuplex_clone = deepcopy(tuplex)
tuplex_clone[2].append(60)
print(tuplex_clone)
print(tuplex)
Ex80 In Python how to know the number of times an item has been repeated
#Create a Tuple tuplex = 2, 4, 5, 6, 2, 3, 4, 4, 9 print(tuplex) #Return the number of items it appears in the tuple. count = tuplex.count(4) print(count) count = tuplex.count(9) print(count) count = tuplex.count(2) print(count)
Ex81 Remove an item from a tuple
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = "c", "e", 3, 1, 2, "H", "E", "L", "L", "O"
#Using merge of tuples with the + operator you can remove
tuplex = tuplex[:2] + tuplex[3:]
print(tuplex)
#Coverting the tuple to list
listx = list(tuplex)
print(listx)
#Remove an item of the list
listx.remove("L")
#Converting the list to tuple
tuplex = tuple(listx)
print(tuplex)
listx.remove("O")
tuplex = tuple(listx)
print(tuplex)
Ex82 Slice a tuple
#Create a tuple tuplex = (2, 4, 3, 5, 4, 6, 7, 8, 6, 9) #Used tuple[start:stop] the start index is inclusive and the stop index _slice = tuplex[3:5] print(_slice) _slice = tuplex[:6] print(_slice) _slice = tuplex[5:] print(_slice) _slice = tuplex[:] print(_slice) _slice = tuplex[-8:-4] print(_slice)
Ex83 The size of the tuple
tuplex = tuple("ce312programming")
print(tuplex)
#Use the len() function to know the length of tuple.
print(len(tuplex))
Ex84 Find the index of an item of the tuple
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = tuple("index tuple")
print(tuplex)
index = tuplex.index("p")
print(index)
index = tuplex.index("p", 5)
print(index)
index = tuplex.index("e", 3, 6)
print(index)
Ex85 Modify items of a tuple
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = ("c","e",3,1,2,[],False)
print(tuplex)
tuplex[5].append(300)
print(tuplex)
Ex86 How operators + and * are used with a Python tuple?
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = 5,
#The * operator --> repeat
print(tuplex * 6)
tuplex = (5, 10, 15)*4
print(tuplex)
#Create three tuplex
tuplex1 = (3, 6, 9, 12, 15)
tuplex2 = ("c", "e", 3, 1, 2, "H", "E", "L", "L", "O")
tuplex3 = (True, False)
#The + operator --> join
tuplex = tuplex1 + tuplex2 + tuplex3
print(tuplex)
Ex87 Slice of a tuple using step parameter
#Create a Tuple
tuplex = tuple("HELLO PYTHON")
print(tuplex)
#Slice --> tuple[start:stop:step]
_slice = tuplex[2:9:2]
print(_slice)
_slice = tuplex[::4]
print(_slice)
_slice = tuplex[9:2:-4]
print(_slice)
_slice = tuplex[9:2:-3]
print(_slice)
11. Python Sets
Ex88 Create a set in Python
#A new empty set setx = set() print(setx) #A non empty set n = set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) print(n)
Ex89 Iteration Over Sets
num_set = set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) for n in num_set: print(n)
Ex90 Add member(s) in Python set
#A new empty set
color_set = set()
#Add a single member
color_set.add("Red")
print(color_set)
#Add multiple items
color_set.update(["Blue", "Green", "White", "Yellow", "Pink", "Black"])
print(color_set)
Ex91 Remove item(s) from Python set
num_set = set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) num_set.pop() print(num_set) num_set.pop() print(num_set) num_set.remove(4) print(num_set) num_set.discard(5) print(num_set)
Ex92 Intersection, Union of sets and Set, Symmetric Difference
#Intersection of Sets setx = set(["GREEN", "BLUE"]) sety = set(["BLUE", "YELLOW"]) setz = setx & sety print(setz) #Union of Sets seta = setx | sety print(seta) #Set Difference setb = setx - setz print(setb) #Symmetric Difference setc = setx ^ sety print(setc) #Issubset and Isscuperset issubset = setx <= sety print(issubset) issuperset = setx >= sety print(issuperset) #Shallow copy of sets setd = setx.copy() print(setd) #Clear sets sete = setx.copy() print(sete) sete.clear() print(sete)
12. Python user-defined functions
Ex93 Call a function
#Call a Function
def avg_number(x, y):
print("Average of ",x," and ",y, " is ", (x+y)/2)
avg_number(3,4)
#Function without Arguments
def printX():
print("This is Python Programming")
print("This is Python Programming")
print("This is Python Programming")
print("Function without Arguments")
printX()
#The Return Statement Function
def nsquare(x, y = 2):
return (x*x + 2*x*x + y*y)
print("The Reurn Statement Function\n")
print("The square of the sum of 2 and 2 is : ", nsquare(2))
print("The square of the sum of 2 and 4 is : ", nsquare(2,4))
#Arbitrary Argument Lists
def sum(*numbers):
s = 0
for n in numbers:
s += n
return s
print("Arbitrary Argument Lists\n")
print(sum(1,2,3,4))
#Lambda Forms
def average(x, y):
return (x + y)/2
print("Lambda Forms\n")
print(average(4, 3))
print((lambda x, y: (x + y/2)(4, 3)))
Aj.NesT Python Colab on GitHub Gist